|
What is a lymph node and what does it do?
Dr Sanjeev Jalihal, a Consultant Haematologist
from Scunthorpe and Goole NHS Trust, Scunthorpe, North
Lincolnshire replies:
What are lymph nodes?
 Lymph
nodes or glands are fleshy pea sized structures found in
groups or chains throughout the body. The nodes in the
neck, armpits and the groins are easily felt; the
diagram below shows their distribution. They are linked
by special lymph channels that ultimately drain into the
blood going to the right side of the heart. Lymph
nodes or glands are fleshy pea sized structures found in
groups or chains throughout the body. The nodes in the
neck, armpits and the groins are easily felt; the
diagram below shows their distribution. They are linked
by special lymph channels that ultimately drain into the
blood going to the right side of the heart.
Lymph nodes serve largely as a barrier to the spread
of infection. Each lymph node has a capsule and an
internal mass of lymphoid tissue. Several lymph vessels
carry lymphatic fluid into the node (afferent lymphatics),
with a single large vessel (the efferent lymphatic)
carrying the lymphatic fluid back out.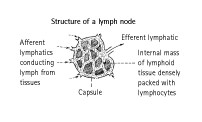
What is "lymph" fluid?
The lymphatic channels drain the excess fluid which
bathes the cells of body
tissues.
This watery looking fluid is called "lymph" and is rich
in protein, lymphocytes, salts and water.
What are the functions
of the lymph glands?
The main function of the lymph glands is to trap
infection and foreign material by acting like a sieve.
The lymphocytes in the nodes produce particular
antibodies that help to fight infection and provide
immunity (resistance) against infection.
What are the functions
of lymphocytes?
There are mainly two sub-types of lymphocytes - 'B'
lymphocytes (B cells) which are produced in the bone
marrow and 'T' lymphocytes (T cells) which are produced
in a specific lymph gland called the 'thymus'.
B cells are responsible for making antibodies.
Antibodies are special molecules, tailor made to react
with foreign material, bacteria, and viruses that enter
the body. Once formed, the antibodies help the body to
eliminate these foreign materials. A proportion of these
cells become 'memory' cells and produce the antibody
again when rechallenged with infection - thus giving
resistance or immunity.
The T lymphocytes have two functions - first they
assist the B cells in producing antibodies, and secondly
they recognise and eliminate cells that seem foreign to
the body. Hence T cells are responsible when an organ
transplant is rejected. T cells are also responsible for
eliminating otherwise normal cells that have been
infected with a virus.
Are there any special
lymphoid tissues?
The spleen and thymus are special lymph nodes that
have more specific function than other lymph nodes. The
lymphocyte aggregates in the bone marrow are also more
specialised.
What are the causes of enlarged lymph nodes?
Bacterial infection such as tonsillitis, infected
cuts and wounds and abscesses are the commonest causes
of enlarged lymph glands. Another common cause is
glandular fever. In these conditions the nodes enlarge
rapidly, are painful and usually disappear when the
infection resolves.
The other common cause of enlarged lymph nodes is
cancer. Cancers of the breast, lung, stomach, throat and
melanoma (a type of skin cancer) commonly seed into
nearby lymph glands. These types of cancer cells may be
trapped by the sieve like action of the lymph nodes -
resulting in secondary cancers occurring in the nodes.
Lymphoma cells are cancer cells produced within the
lymphatic system.
What is lymphoedema?
The term lymphoedema is used to describe swelling of
a part of the body due
to
obstruction to the flow of the lymph. This is commonly
seen in the arm following surgery for breast cancer when
the lymph glands in the armpit are removed. It is also
sometimes seen after treatment for lymphoma following
radiotherapy and occasionally following lymph node
biopsy. Lymphoedema occurring after surgery and
radiotherapy may be difficult to treat and resolve but
can be helped by the use of compression bandages
obtainable through the consultant or the GP. |
![]()
![]()

![]()